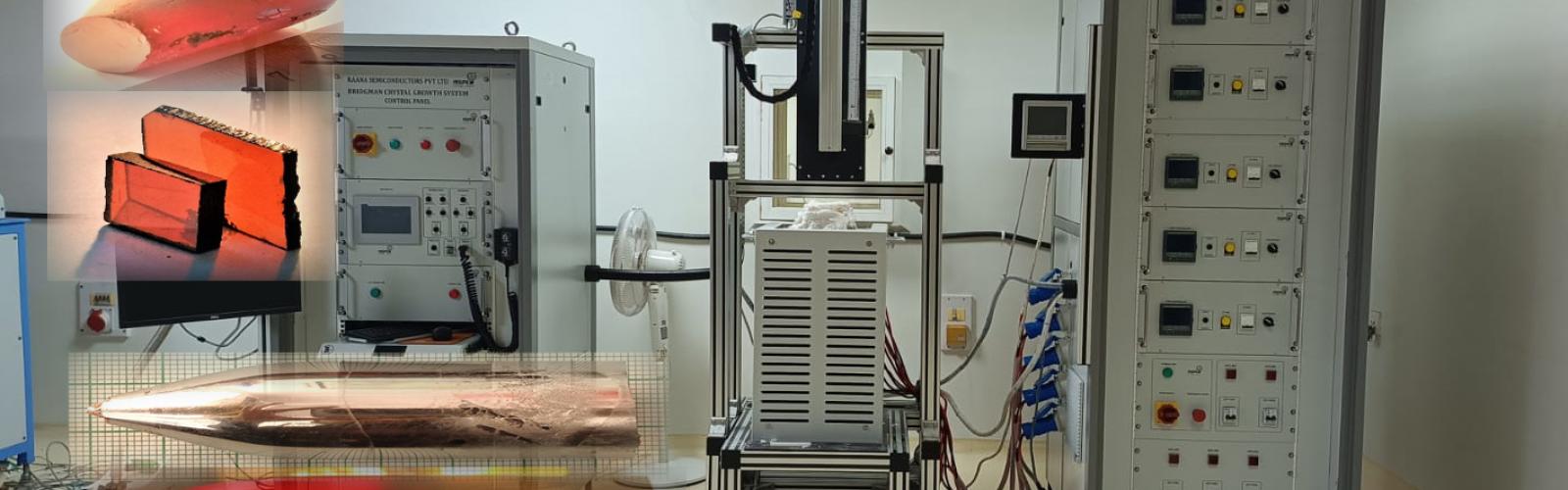
Dedicated to the furtherance of competent research and development in the firmament of Electronic Materials, the Centre for Materials for Electronics Technology (C-MET) functions as an autonomous scientific society under Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology (MeitY), Govt. of India. Besides augmenting core competence, C-MET envisions attainment of self-sufficiency in the sphere of Electronic materials, components and devices to cater to India’s strategic and industrial applications, exploiting indigenous resources of raw materials.
................more

Shri. E Magesh,
Director General
(Additional Charge)
MESSAGE
R & D Activities
Replacement of electronic equipment is very often necessary, due to the rapid technological progress, leading to huge amounts that end up as waste.
C-MET has been working in the area of Low Temperature Co-Fired Ceramic (LTCC) since year 2006. LTCC is a multilayer fabrication process in glass-ceramic regime that primarily creates high density circuit boards with integrated passive components.
- University of Leeds, UK
- Institute of electronics - Bulgarian academy of sciences (IE-BAS), Bulgaria
- Kobe University, Japan
- Garcia University, Slovenia
- National University of Singapore, Singapore
- University of Aveiro, Portugal
Materials for Renewable Energy
Nanomaterials and nanostructures play a critical role in the recent advancement of some of the key technologies associated with energy conversion and storage.
C-MET Pune is developing materials and prototypes for different chemical sensors such as hydrogen, NOx and VOCs based on semiconductor materials for operating at high temperature as well as room temperature.
Centres
HQ cum Pune Laboratory

CMET's R&D activities have been implemented in three laboratories at Pune, Hyderabad and Thrissur. The laboratory at Pune functions as headquarters and extends central coordination support. Each of these laboratories has its own areas of specialization with requisite infrastructure and expertise. This approach has proven to be successful in creating core competence at each laboratory.
PUNE LABORATORY
Li-ion batteries, LTCC Packaging materials, Specialty Polymers, Nano-materials/composites
Hyderabad Laboratory

Ultra Pure Materials: E-Waste and RoHS compound semiconductors, Ultra High Pure Metals and Semiconductors; Refractory Metals, alloys and Special Materials
Thrissur Laboratory

Electronic Ceramics: Microwave dielectrics, Multilayer Ceramics, Actuators and Sensors, Nanomaterials and thin films, Aerogels and Graphene super capacotors
RoHS Services
Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) Test Facility
E- waste (Management and Handling) Rules, 2011, published in the Gazette of India, section 3, sub-section (ii), vide number S.O. 1035(E), have been revised as E-Waste (Management) Rules, 2016 and have come into force from the 1st day of October, 2016. These rules shall apply to every manufacturer, producer, consumer, bulk consumer, collection centres, dealers, e-retailer, refurbisher, dismantler and recycler involved in manufacture, sale, transfer, purchase, collection,
storage and processing of e-waste or electrical and electronic equipment listed in Schedule I, including their components, consumables, parts and spares which make the product operational. Chapter - V of E-waste (Management) Rules – 2016 deals with Reduction in the use of hazardous substances (RoHS) Directive. Every producer of electrical and electronic equipment and their components or consumables or parts or spares listed in Schedule - I shall ensure that, new Electrical and Electronic Equipment and their components or consumables or parts or spares do not contain Lead, Mercury, Cadmium, Hexavalent Chromium, polybrominated biphenyls and polybrominated diphenyl ethers beyond a maximum concentration value of 0.1% by weight in homogenous materials for lead, mercury, hexavalent chromium, polybrominated biphenyls and polybrominated diphenyl ethers and of 0.01% by weight in homogenous materials for cadmium. Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) shall conduct random sampling of electrical and electronic equipment placed on the market to monitor and verify the compliance of Reduction of Hazardous Substances provisions and the cost for sample and testing shall be borne by the Producer. If the product does not comply with Reduction of Hazardous Substances provisions, the producers shall take corrective measures to bring the product into compliance and withdraw or recall the product from the market, within a reasonable period as per the guidelines of the Central Pollution Control Board.
C-MET, Hyderabad laboratory has established state of the art characterization facilities for the analysis of electronic and related samples to quantify the substances banned under Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS), Directive. C-MET has developed requisite Infrastructure, state of the art characterization facilities and Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) as per IEC 62321 standard. RoHS analysis of variety of samples are being carried out using Energy Dispersive X-ray Fluorescence Spectrometer (EDXRF), Atomic Absorption Spectrometer (AAS) with Hydride generator, Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometer (ICPMS), Gas Chromatography Mass Spectrometer (GCMS), Ion-Chromatograph (IC), UV-Visible Spectrophotometer (UV-Visible), etc. This RoHS test facility is accredited as per ISO 17025:2005 standard by National Accreditation Board for Testing & Calibration Laboratories (NABL), Department of Science & Technology, Government of India, with certificate No: T-1780 in the field of chemical analysis of electronic materials (polymers, metals, etc.). In addition to NABL accreditation , C-MET is also having Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS), Govt. of India recognition for testing mercury levels in CFLs and Fluorescent Lamps(FLs) as per test method IS 15906.
This is the only RoHS testing facility in the country established with the aegis of Min. of Electronics & IT (MeitY), Government of India. On Feb. 17, 2017 C-MET and CPCB have signed the MoU to use the RoHS testing facilities of C-MET, Hyderabad for the RoHS compliance testing of EEE products collected in the random sampling from the market in the country.
more details ....... click here

Centre of Excellence (CoE) in E-Waste Management
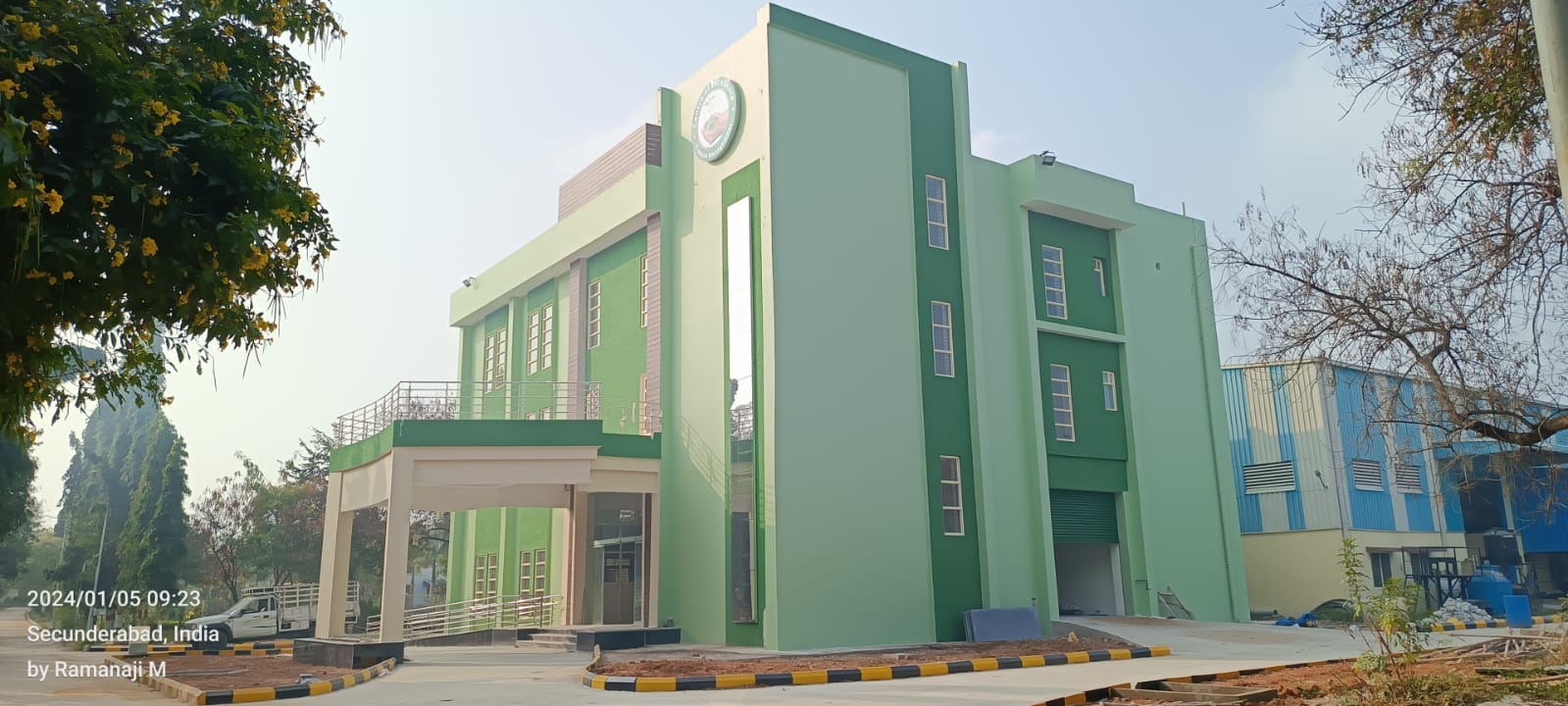

About CoE
Centre of Excellence (CoE) in E-Waste Management has been established to create a self-sustaining ecosystem capable of processing India’s e-waste. It is a joint initiative by Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY), Govt of India in partnership with Government of Telangana (GoT) and the industry.
Objectives of CoE
Facilitate partnership with the industry, start ups, academia and government to translate ideas into products and build affordable technologies
Conduct training/workshops to educate and train human resources already engaged or seeking employment in the areas of recycling, refurbishing, dismantling, etc.
Establish necessary infrastructure to enable R&D, Innovation, Product Development, and Testing for researchers, entrepreneurs, early start-ups, and SMEs
Drive e-waste recycling and refurbishing to support “Swachh Bharat Mission” and “Make in India”